BEIRUT (Reuters) – The future of Kurdish-led areas of northern and eastern Syria has been thrown into doubt by President Donald Trump’s decision to withdraw U.S. troops who have helped to secure the region.
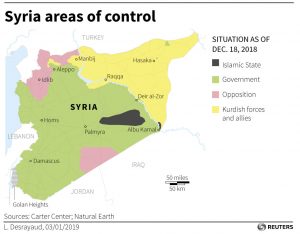
Amounting to about one-quarter of Syria, the area is the largest chunk of territory still outside the control of President Bashar al-Assad, who is backed by Russia and Iran.
Trump said on Wednesday the United States would withdraw slowly “over a period of time” and would protect the U.S.-backed Kurdish fighters as Washington withdraws troops, but without giving a timetable.
Syrian Kurdish leaders fear Turkey will use the withdrawal as an opportunity to launch an assault.
As a result, they are in contact with Moscow and Damascus in the hope of agreeing with arrangements to protect the region from Turkey while also aiming to safeguard their political gains.
HOW DID THE KURDS EMERGE AS A FORCE?
The main Syrian Kurdish faction, the Democratic Union Party (PYD), began to establish a foothold in the north early in the war as government forces withdrew to put down the anti-Assad uprising elsewhere. An affiliated militia, the People’s Protection Units (YPG), secured the region.
Early in the conflict, their control was concentrated in three predominantly Kurdish regions home to roughly 2 million Kurds. Kurdish-led governing bodies were set up.
The area of YPG influence expanded as the YPG allied with the U.S.-led coalition against Islamic State (IS), becoming the spearhead of a multi-ethnic militia, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF).
SDF influence widened to Manbij and Raqqa as IS was defeated in both. It has also reached deep into Deir al-Zor, where the SDF is still fighting IS.
Kurdish leaders say their aim is regional autonomy within a decentralized Syria, not independence.
WHY DOES TURKEY VIEW THEM AS A THREAT?
The PYD is heavily influenced by the ideas of Kurdish leader Abdullah Ocalan, a founding member of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK), which has waged a 34-year insurgency in Turkey for Kurdish political and cultural rights. Ocalan has been in jail since 1999 in Turkey. He is convicted of treason.
The PKK is designated a terrorist organization by Turkey, the United States and the European Union. Turkey says the PKK is indistinguishable from the PYD and YPG.
Turkey has a Kurdish minority equal to 15 to 20 percent of its population, mostly living in eastern and southeastern areas bordering Syria. Wary of separatistism, Turkey views the PYD’s Syrian foothold as a national security threat.
Syria’s main Kurdish groups do not hide Ocalan’s influence: they organized elections towards establishing a political system based on his ideas.
Turkey has already mounted two cross-border offensives in northern Syria as part of its efforts to counter the YPG.
FOR KURDS, IS ASSAD A FRIEND OR FOE?
Syria’s Baathist state systematically persecuted the Kurds before the war. Yet the YPG and Damascus have broadly stayed out of each other’s way during the conflict, despite occasional clashes. They also have been seen to cooperate against shared foes, notably in and around Aleppo.
The YPG has allowed the Syrian state to keep a foothold in its areas. The YPG commander told Reuters in 2017 it would have no problem with the Assad government if Kurdish rights are guaranteed in Syria.
But Damascus opposes Kurdish autonomy demands: the Syrian foreign minister last month said “nobody in Syria accepts talk about independent entities or federalism”.
Talks between the sides last year made no progress.
The Kurdish-led authorities are launching a new initiative aiming to put pressure on the government to reach a political settlement “within the framework of a decentralized Syria,” leading Kurdish politician Ilham Ahmed said last week.
Analysts say the Kurds’ negotiating position has been weakened by Trump’s announcement.
WHAT WOULD AN ASSAD-KURD DEAL MEAN FOR THE WAR?
The territory held by Damascus and the Kurdish-led authorities accounts for most of Syria. A political settlement – if one could be reached, perhaps with Russian help – could go a long way to stitching the map back together.
But it would not mark the end of the war.
Anti-Assad insurgents, though defeated across much of Syria by the government and its allies, still have a foothold in the northwest stretching from Idlib through Afrin to Jarablus. Turkey has troops on the ground in this area.
The rebels include Turkey-backed Free Syrian Army groups and jihadists.
Enmity runs deep between the YPG and these groups.
For the YPG, one priority is recovering Afrin from the rebels who seized it in a Turkey-backed offensive last year.
Assad also wants Turkey out as he vows to recover “every inch” of Syria.
(Writing by Tom Perry; Editing by Angus MacSwan)