By Dan Levine, Benjamin Lesser and Renee Dudley
NEW YORK (Reuters) – Cristina Chen-Oster, a senior salesperson in Goldman Sachs’s convertible bonds department, was a few years out of MIT when a male colleague pinned her against a wall, kissed her, groped her and tried to engage in a sexual act, she said in a lawsuit in federal court. After reporting the incident to her boss, the lawsuit alleged, she missed out on pay and promotions while her accused attacker steadily rose through the ranks.

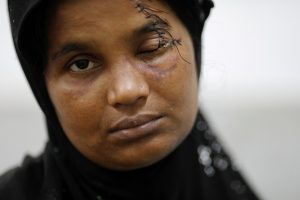
Cathy Sellars at her home in Fort Walton Beach, Florida, U.S. December 21, 2017. REUTERS/Michael Spooneybarger
Cathy Sellars, a 59-year-old mother of two adult children, was training to become a truck driver for freight hauler CRST when she complained to her bosses about repeated sexual harassment by male colleagues, according to a class action lawsuit against the company. Her complaints ignored, she says in court records, she eventually found herself in a truck cab with a male driver who pulled a knife on her after she rebuffed his sexual advances. He then refused to allow her to exit the truck during a trip through the southwest and held her for several hours, she sai
And Sebastian Kelly, a gay driver for an ambulance company in Alabama, said in a lawsuit that he worked in a sexually charged atmosphere, where two male co-workers routinely exposed their genitalia.
News headlines of late have focused on sexual harassment accusations against movie mogul Harvey Weinstein, former Today show anchor Matt Lauer, former U.S. Senator Al Franken and other media figures, entertainers and politicians. In each case, the accusers say they waited years to confront the men who accosted them, most of them too ashamed or fearful to complain publicly or persuaded to keep quiet by tactics meant to suppress the truth.
But these three plaintiffs, and many like them, chose to confront their alleged abusers and hold the companies they work for accountable in public court. Rather than opening the incidents to full public scrutiny, however, judges let companies push the legal boundaries of what should be considered confidential and to keep details of abusive behavior secret.
A Reuters review of federal court cases filed between 2006 and 2016 revealed hundreds containing sexual harassment allegations where companies used common civil litigation tactics to keep potentially damning information under wraps. Plaintiffs in some cases say companies sought to conceal internal documents that reveal similar harassment claims, as well as corporate policies that favored abusers over victims.
In one case, plaintiff lawyers collected secret evidence about alleged criminal behavior, including details of a pharmaceutical saleswoman who alleged a doctor sexually assaulted her at a work-related event. Her supervisor admitted to giving a sheriff’s detective false information about the allegations, court records show.
THE COST OF SECRECY
The true number of such cases is likely much greater than the hundreds identified by Reuters. Federal courts categorize sexual harassment within a larger group of gender discrimination claims, which makes a full accounting difficult. In addition, many sexual harassment cases are filed in state courts. Reuters focused its review on the federal courts because records are more accessible and consistent.
As a result of the sealed documents, cases that could shine light on specific abusers, or on toxic corporate cultures, do the opposite: They enable the very secrecy and corporate complicity that allow sexual harassment to persist in the workplace.
Shira Scheindlin, a former Manhattan federal judge, said judges should make public human-resources complaints that result in employee discipline.

Shira Scheindlin, a former Manhattan federal judge, poses for a portrait at her firm’s office in New York City, U.S., January 8, 2018. Picture taken January 8, 2018. REUTERS/Brendan McDermid
“Otherwise, you get the serial abuser just doing it at the next job,” said Scheindlin, who currently heads the American Bar Association’s federal courts subcommittee and whose private practice includes advising companies on handling sexual harassment complaints. “If that record had been available, there would have been no next job.”
U.S. District Judge Charles Breyer said courts are going too far in routinely sealing such cases. Documents filed in federal court are presumed to be public, he said, so people can understand how the judiciary works. Companies should not be allowed to cloak evidence just because it is damaging, said the judge, based in San Francisco. That goes not only for sexual harassment but also for broader corporate governance issues.
“It’s hard to see why their private interests to avoid embarrassment trumps the public’s right to have access to litigation,” Breyer said.
Companies say they have good reason to seek broad protective orders. They frequently argue that their internal documents contain unproven allegations that shouldn’t be public, or sensitive business information that could aid a competitor. Plaintiff attorneys say they often agree to protective orders and motions to seal information from public disclosure because fighting over public access can increase the length and cost of a lawsuit.
Many judges, meanwhile, are reluctant to enforce transparency when neither side has requested it, according to several current and former federal judges.
“I don’t think any judge is presumptively hostile to the idea of disclosure,” Breyer said. “We may be presumptively hostile to doing more work. I’m speaking for myself.”
Most civil cases settle before they can be publicly aired before a jury. That means the pre-trial secrecy allows companies to permanently conceal information about their sexual harassment policies and how they respond to specific complaints of abuse.
A broad protective order in the ongoing lawsuit by Chen-Oster and three other women against Goldman has allowed the Wall Street giant to keep hundreds of documents under wraps for three years.
Asked about the secrecy, a Goldman spokesperson told Reuters the firm keeps details private because it promises employees confidentiality when they report concerns. The spokesperson would not discuss the specific allegations raised by Chen-Oster and the other plaintiffs.
In court documents, the company acknowledges that Chen-Oster told her boss about the contact with her co-worker and that the supervisor contacted Goldman’s human resources department about it. Chen-Oster, the company says in court filings, did not want to pursue a human resources complaint.
The protective order permitted lawyers on either side to mark any document exchanged in discovery as confidential, thus barring anyone from disclosing it outside the case. Such orders have become standard to ensure secrecy during the pre-trial evidence discovery phase in U.S. civil litigation.
There are no nationwide standards on what information should be sealed when discovery documents are later filed in court. Several federal appeals courts recognize that trade secrets, sensitive financial data, or personal information like Social Security Numbers can remain secret. When it comes to allegations of misconduct, some case law allows information that would intrude on an individual’s privacy to be kept secret. But it is left to judges to decide if someone’s privacy outweighs the public’s interest in disclosure.
Initially, Chen-Oster’s lawyers agreed to the protective order, but later, when they sought to broaden the case, they took the rare step of arguing that many documents filed in court should be made public.
Adam Klein, one of her lawyers, said plaintiff attorneys usually agree to protective orders to gain access to company documents in the first place.
“It’s balancing the interest of the client to get information with the public’s right to know,” Klein said. In Chen-Oster’s case, Klein said, they later pushed to unseal documents in part so that more women working at Goldman who could join the lawsuit would know the details.
The lawyers asked then-U.S. Magistrate Judge James Francis IV in Manhattan to certify the lawsuit as a class action to address pay and promotions lost to gender discrimination at Goldman. To support their request, they filed, under seal, nearly 300 internal Goldman documents the company had given them during discovery. Some of those documents, the lawyers alleged, showed that Goldman rewarded men who engaged in sexual misconduct. Because Goldman had asserted confidentiality during discovery, Chen-Oster’s lawyers had to file those documents in secret.
The plaintiffs also secretly filed a chart that logged gender discrimination complaints Goldman female employees made to the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.
MYSTERY RULING
The plaintiffs’ first request in 2014 to unseal is itself not public, nor is Goldman’s response. Francis sided with Goldman – though his reasoning is unknown because he also sealed the ruling from disclosure on the public court docket.
In a subsequent filing, Chen-Oster’s lawyers argued that details about Goldman HR investigations should be made public, at least without revealing employee names, because they did not contain the type of trade secrets that legal precedent allows companies to keep confidential.
In response, Goldman attorneys argued the documents should remain secret, arguing many contained hearsay and violated the privacy of people who aren’t parties to the suit. The material had been “selectively culled” from Goldman’s internal personnel files to “sensationalize this proceeding,” Goldman’s lawyers said.
U.S. District Judge Analisa Torres in Manhattan reaffirmed Francis’s ruling in 2017, saying the sealed materials “include sensitive content about identifiable non-parties.” Because of that, Torres ruled, the plaintiffs’ request to make the material public should wait until after a judge decides whether to let the case proceed as a class action.
That legal question has now been pending for more than three years.
Torres declined to comment. Francis, who recently left the bench, also declined to comment on the Goldman case. But in general, he said, judges often wait to wade into secrecy issues until after they know what evidence will be important in their rulings. That way they have a roadmap to decide which secret court filings are most relevant to the public, he said.
“Making a decision later with more information may be better,” Francis said. “But later may be much later, and that’s problematic.”
Goldman says in court filings that it takes harassment seriously. Out of 12 human-resources cases highlighted by Chen-Oster’s lawyers, Goldman said it had fired five subjects of those complaints and disciplined five. The identities of those employees, however, are not public, leaving other companies unaware of the abusers’ histories.
Chen-Oster and one other plaintiff declined to talk for this article, and the others did not respond to Reuters’ efforts to reach them.
IDENTITY BLACKOUT
In some cases, companies have persuaded judges to require plaintiffs to keep secret the alleged abusers named in lawsuits, before discovery even begins.
The 2011 claim filed by Sebastian Kelly against his former employer, Regional Paramedical Services Inc of Jasper, Alabama, described a hyper-sexualized environment in which his colleagues allegedly exposed their genitalia regularly and discussed sex in graphic terms. He described one instance in which a colleague told Kelly that he “can’t be gay, you like titties too much.”
That employee’s name, and several others, were blacked out in Kelly’s complaint on the order of Judge James Hancock of the Northern District of Alabama. Hancock ruled that all names of employees who weren’t in supervisory roles, including the human resources director, must be kept secret.
Hancock wrote that allegations against non-supervisory employees are “embarrassing” and that the public’s right to access court records was outweighed by the privacy interests of the employees.
In July 2012, both parties asked the judge to dismiss the case after reaching an out-of-court settlement; the terms weren’t disclosed.
A company spokesperson did not respond to requests for comment. The company denies Kelly’s allegations in court documents. Kelly would not disclose the terms of the settlement.
Because the case did not go to trial, the identities of the accused remain blacked out in Kelly’s lawsuit. The accused are named openly, however, in a complaint Kelly filed with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. Kelly’s lawyers filed the document after Hancock ordered them to submit the EEOC records. Anyone reviewing the filing would find the names of the accused men.
Hancock, who has retired, could not be reached to explain why he did not order the names to be blacked out when the lawyers filed the EEOC complaint.
CLASS SECRETS
In the case against CRST Expedited Inc., a large trucking company, secret court filings were compelling enough to persuade Judge Leonard Strand that plaintiffs had grounds to mount a class action alleging widespread systemic abuse against female employees. Yet even with the class certification, the judge continues to keep important details under wraps.
The case, filed in U.S. District Court in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, centers on the complaints of three women, including Cathy Sellars, the 59-year-old who says she was held at knifepoint after rejecting a coworker’s sexual advances. She said she complained about harassment to her superiors and the human resources department. When she contacted human resources to check on the status of her complaints, she says in her lawsuit, she was told that information was “none of my business.”
After Sellars and the other plaintiffs took CRST to court, their attorneys sought information from the company about how it handled sexual harassment complaints, and how many had been filed. The plaintiffs eventually obtained much of that information.
However, the broad protective order adopted at the beginning of the case – agreed to by both the plaintiffs and the defendants – barred anyone from disclosing that information. The order also forced the plaintiffs to file secretly their motion asking the court for class certification. As a result, all of their allegations of widespread abuse at CRST remained confidential.
Judge Strand granted the plaintiffs’ bid for a class action. In that March order, Strand disclosed some of the sealed material, including the number of female employees – 106 – filing sexual harassment complaints with CRST between October 2013 and February 2016.
But the documents he cited – along with the entire motion he ruled on – still remain under seal.
“The public has a right to know about the gravity of harm in cases like this,” said Giselle Schuetz, an attorney for Sellars. She said she agreed to the sealing, however, because she couldn’t afford to delay the case.
The litigation is pending, and CRST attorney Kevin Visser said he could not discuss the case or any of the specific allegations as a result. The company denied Sellars’ allegations in court documents. Strand did not respond to requests for comment.
CONCEALED EVIDENCE
Plaintiff attorneys say secrecy orders tie their hands even when apparent criminal acts are uncovered during the pre-trial exchange of information, such as evidence that women were sexually assaulted while doing their jobs.
In one gender discrimination claim that went to trial eight years ago, Swiss pharmaceutical giant Novartis attempted to keep secret evidence that one of its managers had given false information to a sheriff’s detective investigating a sexual assault complaint, court records show.
That attempt came to light when the manager testified during a deposition with the plaintiff’s attorneys before the trial. The attorneys could not disclose the revelation to law enforcement authorities without seeking permission from the company or the judge because the deposition was required to be kept secret under the terms of the protective order.
Novartis tried to keep the details under wraps as the case went to trial. The company’s lawyers argued that the alleged sexual assault and the criminal investigation were irrelevant and would prejudice the jury because the details were “unusually graphic and offensive to any reasonable person.”
The judge rejected that argument, so in April 2010, Novartis sales rep Marjorie Salame told the jury that she was sexually assaulted by a doctor at a work-related golf event.
Salame testified that she had considered herself on a management track and enjoyed a good relationship with her boss when she headed to a country club near Tampa, Florida, in May 2002. At the end of the night, Salame said at an earlier deposition, Dr. Edwin Colon got her alone, lifted her skirt and penetrated her with his fingers.
The next day, Salame told her manager, Joseph Simmons, what had happened. Simmons told the jury he also received a phone call from Colon, who was apologetic but denied culpability, saying he had been drinking. The doctor said the sexual contact with Salame had been consensual, Simmons testified.
Colon declined to discuss the case with Reuters. Simmons also declined to comment.
Salame reported the incident to the sheriff’s office, and investigators interviewed Simmons. The Novartis manager told a detective that the doctor had not said he had been drinking and that Novartis was not investigating the matter, court records state. In fact, Simmons later testified, a human resources employee at Novartis was looking into the complaint, a fact he knew when he talked with the detective.
Salame’s ex-manager testified both in the pre-trial deposition and during the jury trial that he had misinformed the detective about what Colon told him and about Novartis investigating the complaint, though he told the jury he had not deliberately lied.
The doctor was not charged with a crime.
Had Salame’s lawyers wanted to tell law enforcement authorities about Simmons’ pre-trial revelation, they would have had to go through an elaborate process with Novartis and the judge. Nothing on the court docket shows they did so. Katherine Kimpel, who represented Salame and other women against Novartis, declined to comment.
U.S. Senator Richard Blumenthal, a Democrat, co-sponsored legislation in 2014 that would have allowed victims to disclose evidence obtained in civil litigation to law enforcement, if it impacts public health or safety. The bill died in committee.
Broad protective orders and motions to seal, Blumenthal said, can often conceal evidence of criminal behavior, allowing abusers to prey on unsuspecting women.
“The present practice sends her on a trail where all of the warning signs about the dangers have been removed, and she’s there vulnerable and alone,” he said.
Salame told Reuters she was too overwhelmed to pursue the matter involving her supervisor after learning he had misled investigators. She did file a civil lawsuit against the doctor, who denied her allegations. Three years ago, both sides agreed to a settlement.
The manager’s testimony was the first time Salame learned what he had done. “It took eight years for it to come out and vindicate me,” Salame said in an interview.
Few sexual harassment cases reach trial, making the Novartis case – and the details disclosed during public testimony – unusual.
The 2010 trial generated weeks of testimony – and headlines – about how the company treated women. The jury eventually ordered Novartis to pay $250 million in punitive damages in the class action. The company later decided to settle the case and pay about $153 million to class members, rather than appeal the jury verdict.
A Novartis spokesman declined to discuss the case with Reuters.
As part of the resolution of the case, the company agreed to internal reforms, including annual training on a new sexual harassment policy and new measures for tracking and investigating complaints. On pay, it agreed to analyze gender discrepancies and to share the results of that analysis with the plaintiffs’ attorneys.
More than three years later, U.S. District Judge Colleen McMahon congratulated Novartis for successfully complying with the reforms.
Yet even in a case with such transparency, the openness had its limits. The details of Novartis’s compliance efforts were not filed on the court docket and remain secret.
(Reporting by Dan Levine in San Francisco, Benjamin Lesser in New York and Renee Dudley in Boston. Edited by Janet Roberts.)