By Jack Stubbs
MOSCOW (Reuters) – North Korea is preparing to test a long-range missile which it believes can reach the west coast of the United States, a Russian lawmaker just returned from a visit to Pyongyang was quoted as saying on Friday.
Anton Morozov, a member of the Russian lower house of parliament’s international affairs committee, and two other Russian lawmakers visited Pyongyang on Oct. 2-6, Russia’s RIA news agency reported.
“They are preparing for new tests of a long-range missile. They even gave us mathematical calculations that they believe prove that their missile can hit the west coast of the United States,” RIA quoted Morozov as saying.
“As far as we understand, they intend to launch one more long-range missile in the near future. And in general, their mood is rather belligerent.”
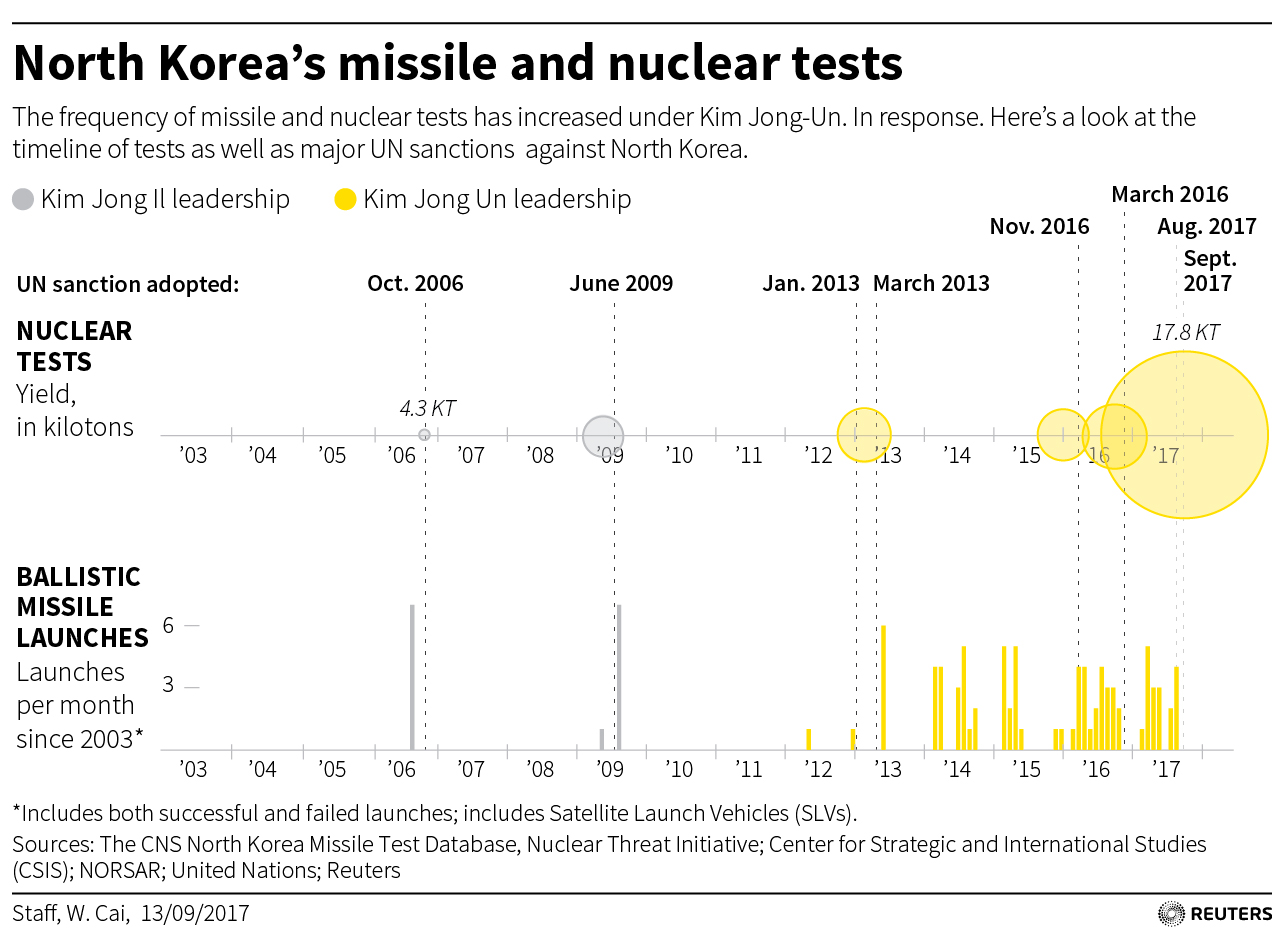
Tensions have risen in recent weeks over North Korea’s nuclear weapons and missile programs as Pyongyang has test-fired several missiles and conducted what it said was a test explosion of a hydrogen bomb as it advances toward its goal of developing a nuclear-tipped missile capable of hitting the U.S. mainland.
Morozov’s comments drove up the price of U.S. Treasury bonds, as investors, worried about the prospect of new North Korean missile tests, moved into assets the market views as a safe haven in times of uncertainty.
Reuters was not able to independently verify Morozov’s account, and he did not specify which North Korean officials had given him the information about the planned test.
In Washington, a U.S. official said that there had been indications that North Korea could be preparing for a missile test on or around Oct. 10, the anniversary of the founding of the ruling Korean Workers Party and a day after the Columbus Day holiday in the United States.
The official, speaking on condition of anonymity, did not disclose the type of missile that could be tested and cautioned that North Korea in the past has not staged launches despite indications that it would.
A senior CIA analyst, speaking at a conference in Washington this week, said the North Korean government likely would stage some kind of provocation on Oct. 10 but did not elaborate on what form it might take.
“There is a clarity of purpose in what (North Korean leader) Kim Jong Un is doing. I don’t think he’s done,” said Yong Suk Lee, the deputy assistant director of the CIA’s Korea Mission Center, which was set up this year. “In fact, I told my own staff (that) October 10th is the Korean Workers Party founding day. That’s Tuesday in North Korea, but Monday – the Columbus Day holiday – in the United States. So stand by your phones.”
Morozov’s delegation had “high-level” meetings in Pyongyang, RIA news agency said, citing the Russian embassy in the North Korean capital.
Tensions over North Korea’s nuclear program have been running high in recent weeks since Pyongyang staged a series of missile tests, and conducted a text explosion on Sept. 3 of what it said was a hydrogen bomb.
There has also been an exchange of tough rhetoric between Pyongyang and Washington.
U.S. President Donald Trump threatened to “totally destroy” North Korea if it threatens the United States. North Korean leader Kim Jong Un responded by calling Trump deranged and saying he would pay dearly for his threat.
China, North Korea’s main ally, has backed sanctions against Pyongyang and on Saturday in response to the Nobel Peace Prize being awarded to the International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons, said it backed a worldwide ban on nuclear weapons.
“China has always supported a complete and total ban on nuclear weapons, but also believes that the goal of achieving nuclear disarmament cannot be achieved overnight and must advance gradually within the existing disarmament mechanism. China is willing to work with all parties to achieve a nuclear-weapon-free world,” said China’s foreign ministry.
“BELLICOSE RHETORIC”
Morozov is a member of the LDPR, a right-wing populist party. It casts itself as an opposition party, but hews close to the Kremlin line on matters of international affairs.
Describing meetings with North Korean officials, Morozov said they “displayed serious determination and bellicose rhetoric,” RIA reported.
“The situation, of course, demands the swiftest intervention of all interested states, particularly those represented in the region, in order to prevent wide-scale military action,” the agency quoted him as saying.
Russia has closer relations with Pyongyang than many other world powers, linked in part to Kim Il Sung, the founder of North Korea and the current leader’s grand-father, having lived for a time in the Soviet Union.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has joined other world powers in condemning North Korea’s weapons program, but has taken a softer line than Western governments.
Putin has said that Pyongyang will not be cowed into giving up its weapons program. He has accused Washington of trying to effect regime change in North Korea, and predicted that would unleash chaos.
U.S. Treasury prices surged on the report of a possible new missile test, pulling yields lower, as investors cut risk out of their portfolios and sought the safety of Treasuries. Treasury prices move inversely to their yields.
Benchmark 10 year U.S. Treasury yields fell from the session high 2.40 percent mark <US10YT=TWEB> to 2.35 percent around midday (1600 GMT) in New York.
“It has just been risk-off buying into the long (Columbus Day) weekend … You look at the charts, it has really been a one-way trade of lower yields,” said Justin Lederer, Treasury analyst at Cantor Fitzgerald in New York.
(Reporting by Jack Stubbs; Additional reporting by Daniel Bases in New York and Idrees Ali and Jonathan Landay in Washington, Ben Blanchard in Beijing; Writing by Christian Lowe; Editing by Toby Chopra and James Dalgleish)