By Jeff Mason and Roberta Rampton
WARSAW (Reuters) – U.S. President Donald Trump vowed on Thursday to confront North Korea “very strongly” following its latest missile test and urged nations to show Pyongyang that there would be consequences for its weapons program.
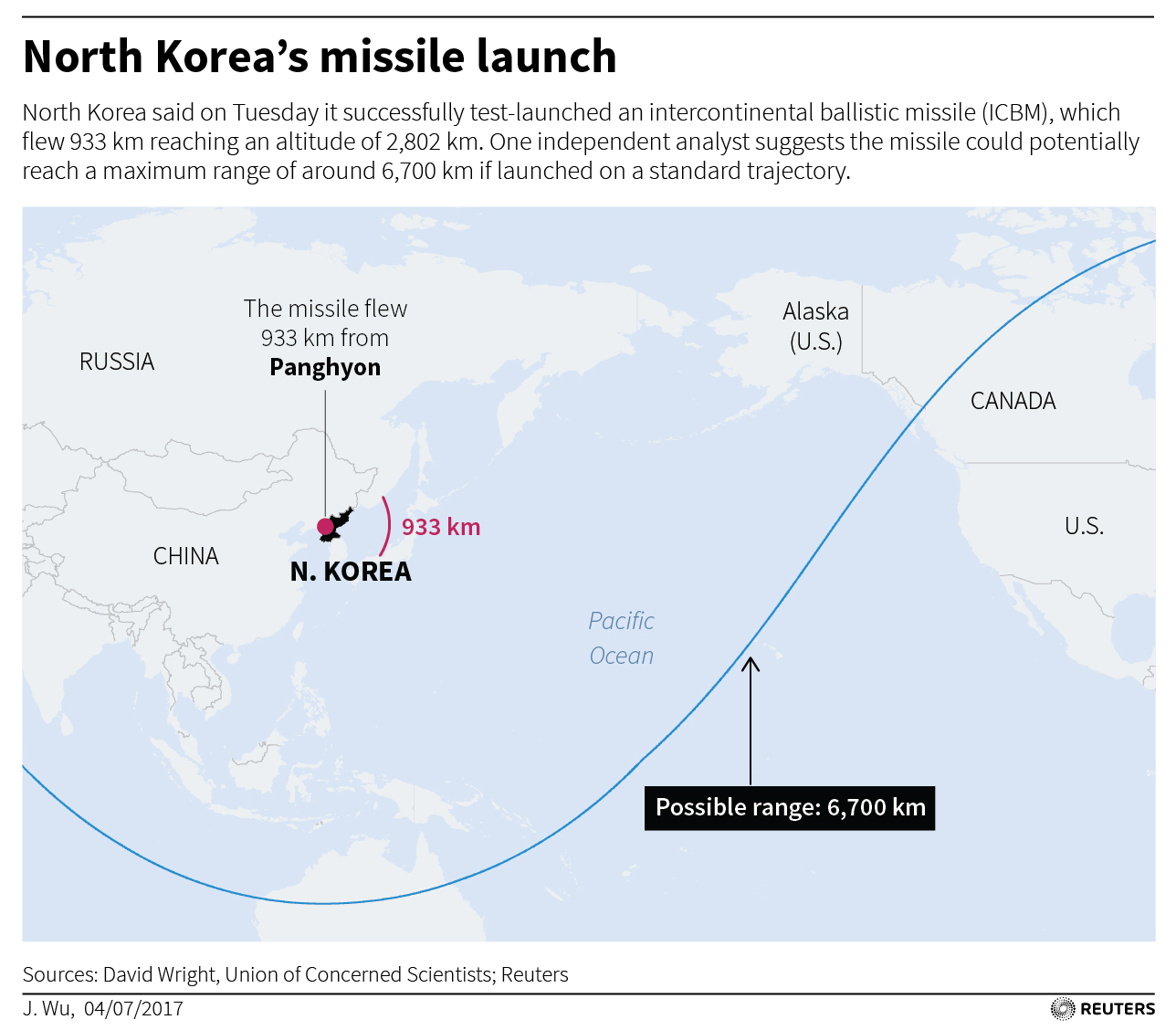
North Korea on Tuesday test-launched an intercontinental ballistic missile that some experts believe has the range to reach the U.S. states of Alaska and Hawaii and perhaps the U.S. Pacific Northwest. North Korea said it could carry a large nuclear warhead.
Speaking at a news conference with Polish President Andrzej Duda, Trump said Korea was “a threat, and we will confront it very strongly”.
He said the United States was considering “severe things” for North Korea, but that he would not draw a “red line” of the kind that his Democratic predecessor, Barack Obama, had drawn but not enforced on the use of chemical weapons in Syria.
Trump added: “… they are behaving in a very, very dangerous manner and something will have to be done.”
The issue presents Trump, who took office in January, with perhaps his biggest foreign policy challenge. It has put pressure on his relationship with Chinese President Xi Jinping, whom Trump had pressed without success to rein in Pyongyang.
The United States said on Wednesday that it was ready to use force if necessary to stop North Korea’s nuclear missile program. But China on Thursday called for restraint and made clear it did not want to be targeted by U.S. sanctions.
Meeting in Germany ahead of a G20 summit, Xi told South Korean President Moon Jae-in that “China upholds the denuclearization of the peninsula, maintaining its peace and stability, resolving the issue via dialogue and consultation, and that all sides strictly abide by relevant resolutions of the U.N. Security Council”, according to the Chinese Foreign Ministry.
And Chinese Vice Finance Minister Zhu Guangyao said that, while China would implement relevant U.N. resolutions, “the U.S. should not use their domestic laws as excuses to levy sanctions against Chinese financial institutions”.
“BAD BEHAVIOR”
Trump flew on to Hamburg on Thursday to attend the summit, and was due to meet with Xi there.
His frustration that Beijing has not done more to clamp down on North Korea prompted him to tweet on Wednesday: “Trade between China and North Korea grew almost 40% in the first quarter. So much for China working with us – but we had to give it a try!”
Trump did not mention China specifically in his remarks in Poland, but his message that other countries needed to do more was clearly meant for Beijing.
“President Duda and I call on all nations to confront this global threat and publicly demonstrate to North Korea that there are consequences for their very, very bad behavior,” he said.
U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations Nikki Haley told the U.N. Security Council on Wednesday that the United States would propose new U.N. sanctions in coming days, and that if Russia and China did not support the move, then “we will go our own path”.
Some diplomats say Beijing has not been fully enforcing existing international sanctions on its neighbor and has resisted tougher measures, such as an oil embargo, bans on the North Korean airline and guest workers, and measures against Chinese banks and other firms doing business with the North.
U.S. officials have said the United States might specifically seek unilaterally to sanction more Chinese companies that do business with North Korea, especially banks – echoing a tactic it used to pressurize to Iran to curb its nuclear program.
South Korean presidential spokesman Park Su-hyun gave a somewhat different account of the Xi-Moon meeting. He told reporters that the two men had agreed North Korea’s missile test was “unforgivable”, and had discussed stepping up pressure and sanctions.
(This story has been refiled to make explicit that Trump was speaking in paragraph 5)
(additional reporting by Marcin Goettig; Editing by Kevin Liffey)