By Jack Kim and Kiyoshi Takenaka
SEOUL/TOKYO (Reuters) – A North Korean state agency threatened on Thursday to use nuclear weapons to “sink” Japan and reduce the United States to “ashes and darkness” for supporting a U.N. Security Council resolution and sanctions over its latest nuclear test.
The Korea Asia-Pacific Peace Committee, which handles the North’s external ties and propaganda, also called for the breakup of the Security Council, which it called “a tool of evil” made up of “money-bribed” countries that move at the order of the United States.
“The four islands of the archipelago should be sunken into the sea by the nuclear bomb of Juche. Japan is no longer needed to exist near us,” the committee said in a statement carried by the North’s official KCNA news agency.
Juche is the North’s ruling ideology that mixes Marxism and an extreme form of go-it-alone nationalism preached by state founder Kim Il Sung, the grandfather of the current leader, Kim Jong Un.
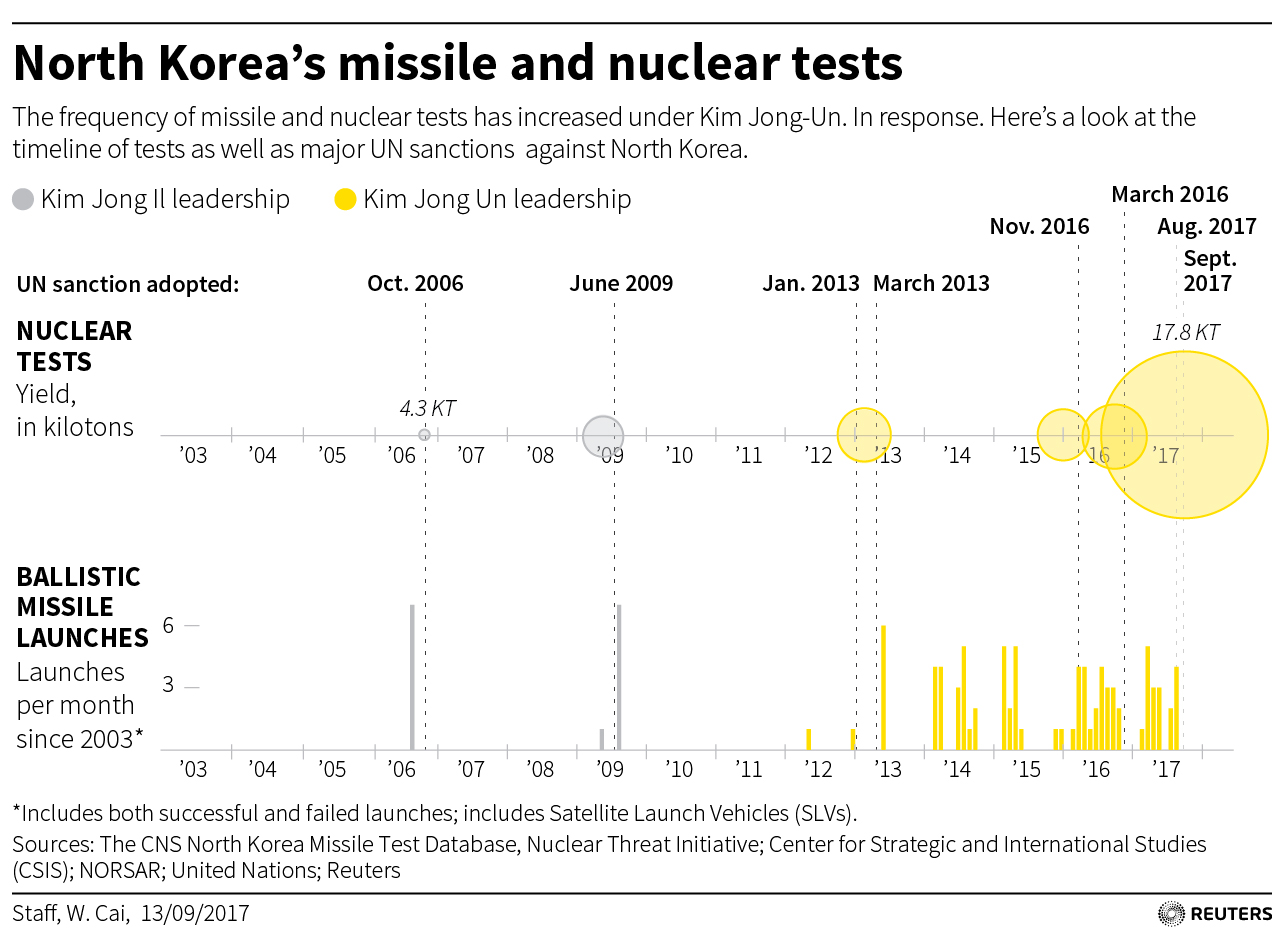
Regional tension has risen markedly since the reclusive North conducted its sixth, and by far its most powerful, nuclear test on Sept. 3, following a series of missile tests, including one that flew over Japan.
The 15-member Security Council voted unanimously on a U.S.-drafted resolution and a new round of sanctions on Monday in response, banning North Korea’s textile exports that are the second largest only to coal and mineral, and capping fuel supplies.
The North reacted to the latest action by the Security Council, which had the backing of veto-holding China and Russia, by reiterating threats to destroy the United States, Japan and South Korea.
“Let’s reduce the U.S. mainland into ashes and darkness. Let’s vent our spite with mobilization of all retaliation means which have been prepared till now,” the statement said.
Japan’s Nikkei stock index and dollar/yen currency pared gains, although traders said that was more because of several Chinese economic indicators released on Thursday rather than a reaction to the North’s latest statement.
South Korea’s won also edged down around the same time over domestic financial concerns.
Despite the North’s threats, South Korean President Moon Jae-in said he was against having nuclear weapons in his country, either by developing its own arsenal or bringing back U.S. tactical nuclear weapons that were withdrawn in the early 1990s.
“To respond to North Korea by having our own nuclear weapons will not maintain peace on the Korean peninsula and could lead to a nuclear arms race in northeast Asia,” Moon said in an interview with CNN.
South Korea’s Unification Ministry also said it planned to provide $8 million through the U.N. World Food Programme and UNICEF to help infants and pregnant women in the North.
The move marks Seoul’s first humanitarian assistance for the North since its fourth nuclear test in January 2016 and is based on a longstanding policy of separating humanitarian aid from politics, the ministry said.
“DANCING TO THE TUNE”
The North’s latest threats also singled out Japan for “dancing to the tune” of the United States, saying it should never be pardoned for not offering a sincere apology for its “never-to-be-condoned crimes against our people”, an apparent reference to Japan’s wartime aggression.
It also referred to South Korea as “traitors and dogs” of the United States.
Japan criticized the North’s statement harshly.
“This announcement is extremely provocative and egregious. It is something that markedly heightens regional tension and is absolutely unacceptable,” Japanese Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshihide Suga told reporters.
Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, visiting India, called for strict enforcement of the U.N. resolution, saying the world must force a change.
The 15-member Security Council voted unanimously on a U.S.-drafted resolution and a new round of sanctions against North Korea on Monday in response to its latest and most powerful test, banning North Korea’s textile exports that are the second largest only to coal and mineral, and capping fuel supplies.
North Korea had already rejected the Security Council resolution, vowing to press ahead with its nuclear and missile programs.
A tougher initial U.S. draft of Monday’s resolution was weakened to win the support of China, the North’s lone major ally, and Russia. Significantly, it stopped short of imposing a full embargo on oil exports to North Korea, most of which come from China.
The latest sanctions also make it illegal for foreign firms to form commercial joint ventures with North Korean entities.
U.S. President Donald Trump has vowed that North Korea will never be allowed to threaten the United States with a nuclear-tipped missile, but has also asked China to do more to rein in its neighbor. China in turn favors an international response to the problem.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Hua Chunying said the international community had reached a “high consensus” on trying to realize a peaceful solution.
“We urge the relevant directly involved parties to seize the opportunity and have the political nerve to make the correct political choice as soon as possible,” Hua told a regular press briefing.
The North accuses the United States, which has 28,500 troops in South Korea, of planning to invade and regularly threatens to destroy it and its Asian allies.
The United States and South Korea are technically still at war with North Korea because the 1950-53 Korean conflict ended with a truce and not a peace treaty.
(Additional reporting by Christian Shepherd in Beijing, Hyonhee Shin in Seoul, Sanjeev Miglani in New Delhi and Kiyoshi Takenaka in Tokyo; Editing by Paul Tait and Nick Macfie)