
By Angus McDowall and Jack Stubbs
BEIRUT/MOSCOW (Reuters) – Russia will establish a humanitarian corridor and implement a five-hour daily truce in Syria’s eastern Ghouta, it said on Monday, after a U.N. Security Council resolution demanding a 30-day ceasefire across the entire country.
Over the past week Syria’s army and its allies have subjected the rebel-held enclave of eastern Ghouta near Damascus to one of the heaviest bombardments of the seven-year war, killing hundreds.
On Sunday health authorities there said several people had suffered symptoms consistent with chlorine gas exposure and on Monday rescue workers and a war monitor said seven small children were killed by air and artillery strikes in one town.
“Eastern Ghouta cannot wait, it is high time to stop this hell on earth,” U.N. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres told the U.N. Human Rights Council in Geneva, calling for implementation of the ceasefire.
Fighting has raged across Syria since Saturday’s resolution, as Turkey presses its offensive against a Kurdish militia in Afrin, rival rebel groups fight each other in Idlib and a U.S.-led coalition targets Islamic State in the east..
Russia’s defense minister was cited by the RIA news agency as saying President Vladimir Putin had ordered a daily ceasefire in eastern Ghouta from 9am to 2pm each day and for the creation of a “humanitarian corridor” to allow civilians to leave.
Russia, along with Iran and Shi’ite militias, is a major backer of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad and it joined the war on his side in 2015, helping him claw back important areas.
The Russian defense minister, Sergei Shoigu, did not say whether the Syrian government or other allied forces had agreed to abide by the five-hour daily truce.
Mohamad Alloush, the political chief of one of eastern Ghouta’s biggest rebel factions, said the Syrian army and its allies had launched “a sweeping ground assault” after the U.N. resolution, adding it was vital that the truce be implemented.
“We hope for real, serious, practical action,” he said.
DEATHS
A picture issued by Civil Defence rescue workers, which Reuters could not independently verify, showed seven small bodies lying next to each other, wrapped in white and blue sheets, after air and artillery strikes on the town of Douma in eastern Ghouta.
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a Britain-based war monitor, said four of them were among a single family of nine killed by an air strike. The other three were among seven killed by shelling in the same town, it said.
Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov said allegations the Syrian government was responsible for any chemical attack, after reports of people suffering symptoms of chlorine gas poisoning, were aimed at sabotaging the truce.
The Syrian government has consistently denied using chemical weapons in the war, which will soon enter its eighth year having killed hundreds of thousands of people and forced half of Syria’s pre-war population of about 23 million from their homes.
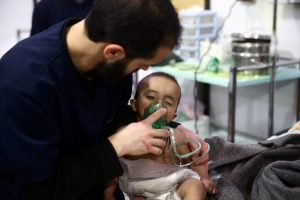
Man with a child are seen in hospital in the besieged town of Douma, Eastern Ghouta, Damascus, Syria February 25, 2018. REUTERS/Bassam Khabieh
The bombardment of eastern Ghouta over the past week has been one of the heaviest of the war, killing at least 556 people in eight days, according to a toll compiled by the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a UK-based war monitor.
The intensity of the bombardment has diminished since the U.N. resolution, the Observatory said, but it added that 21 people had been killed in eastern Ghouta on Monday, including the seven small children in the photograph.
Rebel shelling has caused 36 deaths and a number of injuries in Damascus and nearby rural areas in the last four days, Zaher Hajjo, a government health official, told Reuters.
Speaking in Riyadh, deputy director general of the World Health Organisation, Peter Salama, said the WHO urgently needed to evacuate 750 medical cases from eastern Ghouta.
“We also need sustained access for medical equipment and for medical drugs and commodities,” he said, adding that some supplies had been “systematically removed from convoys”.
RELATIVE LULL
In eastern Ghouta, people were making use of a relative lull in the bombardment to find provisions, said Moayad Hafi, a rescue worker based there.
“Civilians rushed from their shelters to get food and return quickly since the warplanes are still in the sky and can hit at any moment,” he told Reuters in a voice message.
Lavrov said the ceasefire would not cover either the Ahrar al-Sham or the Jaish al-Islam factions, describing them as partners of the former al Qaeda affiliate, the Nusra Front.
The two major rebel factions in eastern Ghouta are Jaish al-Islam and Failaq al-Rahman. Tahrir al-Sham, an alliance of jihadists including Nusra, also has a small presence there.

A young boy rides a bicycle, near damaged houses, after an air raid in the besieged town of Douma, Eastern Ghouta, Damascus, Syria February 23.
REUTERS/Bassam Khabieh
“Partners of al-Nusra are not protected by the ceasefire regime. They are also subject to the legitimate actions of Syrian armed forces and all those who support the Syrian army,” said Lavrov.
In Idlib, Ahrar al-Sham and Tahrir al-Sham have been battling each other in recent days, rather than working in partnership.
Syrian state television reported that army units had advanced against militants near Harasta in eastern Ghouta. State news agency SANA also reported that the army had stopped a car bomb being driven into Damascus.
The Nusra Front has consistently been excluded from ceasefires in Syria, and the opposition says the government has used this as an excuse to keep up its bombardments.
(Additional reporting by Ellen Francis and Dahlia Nehme in Beirut, Stephanie Nebehay in Geneva, Sarah Dadouch in Riyadh and Polina Ivanova in Moscow Editing by Gareth Jones)




