By Mirwais Harooni
KABUL (Reuters) – It took nearly 24 hours for his Afghan family to discover Hamidullah’s broken body on the bottom shelf of a morgue at Kabul’s Wazir Akhbar Khan hospital.
Around him were placed the few personal belongings he had with him when he died.
“He was engaged and was about to get married,” his cousin Abdullah told Reuters, grief clouding his eyes as he stood in the barren morgue. “All of his and his family’s dreams remained unfinished.”
Twenty-year-old Hamidullah was on his way to his print shop in Afghanistan’s capital city early on Wednesday morning when he was killed by a massive truck bomb that exploded in the middle of a busy street, killing at least 80 people and wounding more than 450.
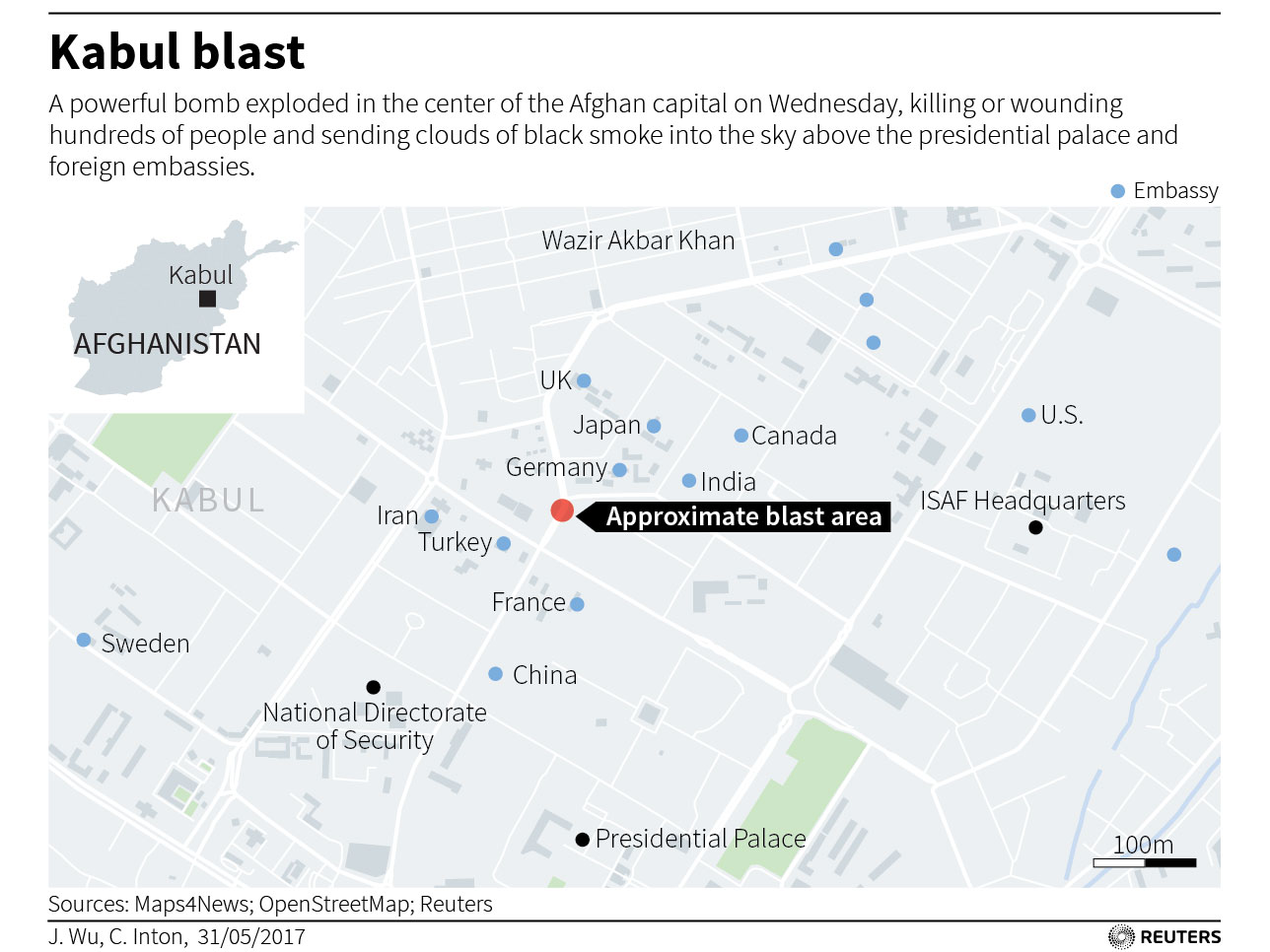
While the intended target of the bomb remains unknown, the explosion occurred near the gates of a heavily fortified area of the city that holds many foreign embassies and government ministries.
Many of the victims, however, were working class Afghans, people who had managed to eke out livelihoods during years of violence and economic malaise.
For Hamidullah’s family, the first indication something was be wrong was the sound of a powerful explosion, followed by an expanding cloud of smoke rising over the city.
Calls to his cellphone went unanswered, and a growing number of extended family members joined huge crowds at hospitals around the city, all seeking news of friends and family caught in the attack.
“We went to several hospitals to find him,” said Abdullah.
The hospital in Wazir Akhbar Khan was one of several inundated with the wounded, and later, the bodies.
“I have never experienced such a day in all my life,” said one morgue attendant who asked for anonymity as he was not authorized to speak publicly. “All the freezers were full, and the dead bodies lined the road to the morgue as well.”
As of Thursday morning, as Hamidullah’s family gathered in small groups under the trees outside the morgue to wait for his father’s arrival, there were still a dozen unidentified bodies at the hospital, officials said.
Among those, around half are unrecognizable, the attendant added. Due to a lack of space, bodies had to be laid out on the ground and 20 were sent to a nearby military hospital.
VICTIMS REMEMBER
Among the victims were employees of Afghan and international media, a major telecommunications company and a bank as well as police officers and security guards.
Kabul’s Emergency Hospital received at least 108 victims of Wednesday’s attack, said Sakhi Shafiq, a team leader there.
From their hospital beds, survivors described the scenes of horror they had lived through.
“I felt my face and body burning and I felt blood coming out of my face,” said Karim Jan, speaking with difficulty.
With chaos all around, he staggered several blocks to Emergency Hospital where he remains, heavily bandaged, with shrapnel scars dotting his face and limbs.
Baqer Zmarai was walking to his job at the state television station and had just passed the German Embassy, which was heavily damaged in the blast, when the bomb went off.
“I fell on the ground,” he said from his bed at Wazir Akhbar Khan hospital. “It was hard to see my surroundings. I could hear people yelling for help.”
Surrounded by dirt, smoke, mangled cars and shattered buildings, Zmarai struggled to stand on injured legs.
“I tried to escape but I could not walk.”
While some of the wounded were able to go home, many remain in hospitals and the search for lost loved ones continues.
“I do not know if my son is dead or alive. I have to see and find him,” said Besmillah, who stood outside the locked gates of Emergency Hospital on Thursday, pleading with the staff to let him enter.
“I went to every single hospital but could not find my son.”
(Writing by Josh Smith; Editing by Robin Pomeroy)