By Jack Kim and Christine Kim
SEOUL (Reuters) – North Korea said on Wednesday its newly developed intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) can carry a large nuclear warhead, triggering a call by Washington for global action to hold it accountable for pursuing nuclear weapons.
A spokeswoman for the U.S. Defense Department said it had concluded that North Korea test-launched an ICBM on Tuesday, which some experts now believe had the range to reach the U.S. state of Alaska as well as parts of the mainland United States.
U.S. Secretary of State Rex Tillerson said the test, on the eve of the U.S. Independence Day holiday, represented “a new escalation of the threat” to the United States and its allies, and vowed to take stronger measures.
North Korean leader Kim Jong Un said the test completed his country’s strategic weapons capability that includes atomic and hydrogen bombs and ICBMs, the state KCNA news agency said.
Pyongyang would not negotiate with the United States to give up those weapons until Washington abandons its hostile policy against the North, KCNA quoted Kim as saying.
“He, with a broad smile on his face, told officials, scientists and technicians that the U.S. would be displeased … as it was given a ‘package of gifts’ on its ‘Independence Day’,” KCNA said.
Kim ordered them to “frequently send big and small ‘gift packages’ to the Yankees,” it added.
The launch came days before leaders from the Group of 20 nations are due to discuss steps to rein in North Korea’s weapons program, which it has pursued in defiance of United Nations Security Council sanctions.
The test successfully verified the technical requirements of the newly developed ICBM in stage separation, the atmospheric re-entry of the warhead and the late-stage control of the warhead, KCNA said.
Tillerson warned that any country that hosts North Korean workers, provides economic or military aid to Pyongyang, or fails to implement U.N. sanctions “is aiding and abetting a dangerous regime”.
“All nations should publicly demonstrate to North Korea that there are consequences to their pursuit of nuclear weapons,” Tillerson said in a statement.
DIPLOMATIC PRESSURE
U.S. President Donald Trump has been urging China, North Korea’s main trading partner and only big ally, to press Pyongyang to give up its nuclear program.
The U.N. Security Council, currently chaired by China, will hold an emergency meeting on the matter at 3 p.m. EDT (1900 GMT) on Wednesday, following a request by the United States, Japan and South Korea.
Diplomats say Beijing has not been fully enforcing existing international sanctions on its neighbor, and has resisted tougher measures, such as an oil embargo, bans on the North Korean airline and guest workers, and measures against Chinese banks and other firms doing business with the North.
A 2015 U.N. document estimated that more than 50,000 North Korean workers were overseas earning currencies for the regime, with the vast majority in China and Russia.
North Korea appeared to have used a Chinese truck, originally sold for hauling timber, but later converted for military use, to transport and erect the missile on Tuesday.
Trump has indicated he is running out of patience with Beijing’s efforts to rein in North Korea. His administration has said all options are on the table, military included, but suggested those would be a last resort and that sanctions and diplomatic pressure were its preferred course.
Trump is due to meet Chinese President Xi Jinping and Russian President Vladimir Putin during the G20 meeting in Germany this week.
Russia and China joined diplomatic forces on Tuesday and called for North Korea to suspend its ballistic missile program in return for a moratorium on large-scale military exercises by the United States and South Korea.
In Beijing, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Geng Shuang said the joint statement showed the international community wanted dialogue and not antagonistic voices, as he also urged North Korea not to violate U.N. Security Council resolutions.
“We hope relevant counties can maintain calm and restraint, and not take steps that might worsen tensions on the peninsula,” Geng told a daily briefing.
The U.S. and South Korean militaries conducted a ballistic missile test early on Wednesday in a show of force on the east coast of the Korean peninsula. The South said the drill aimed to showcase the ability to strike at the North’s leadership if necessary.
“It’s discouraging that the Chinese (and Russians) are still calling for ‘restraint by all sides’, despite the fact that their client state, North Korea, has cast aside all restraint and is sprinting for the finish line in demonstrating a nuclear-armed ICBM capability,” said Daniel Russel, formerly Washington’s top East Asia diplomat, now a diplomat in residence at the Asia Society Policy Institute.
LONG-RANGE MISSILE
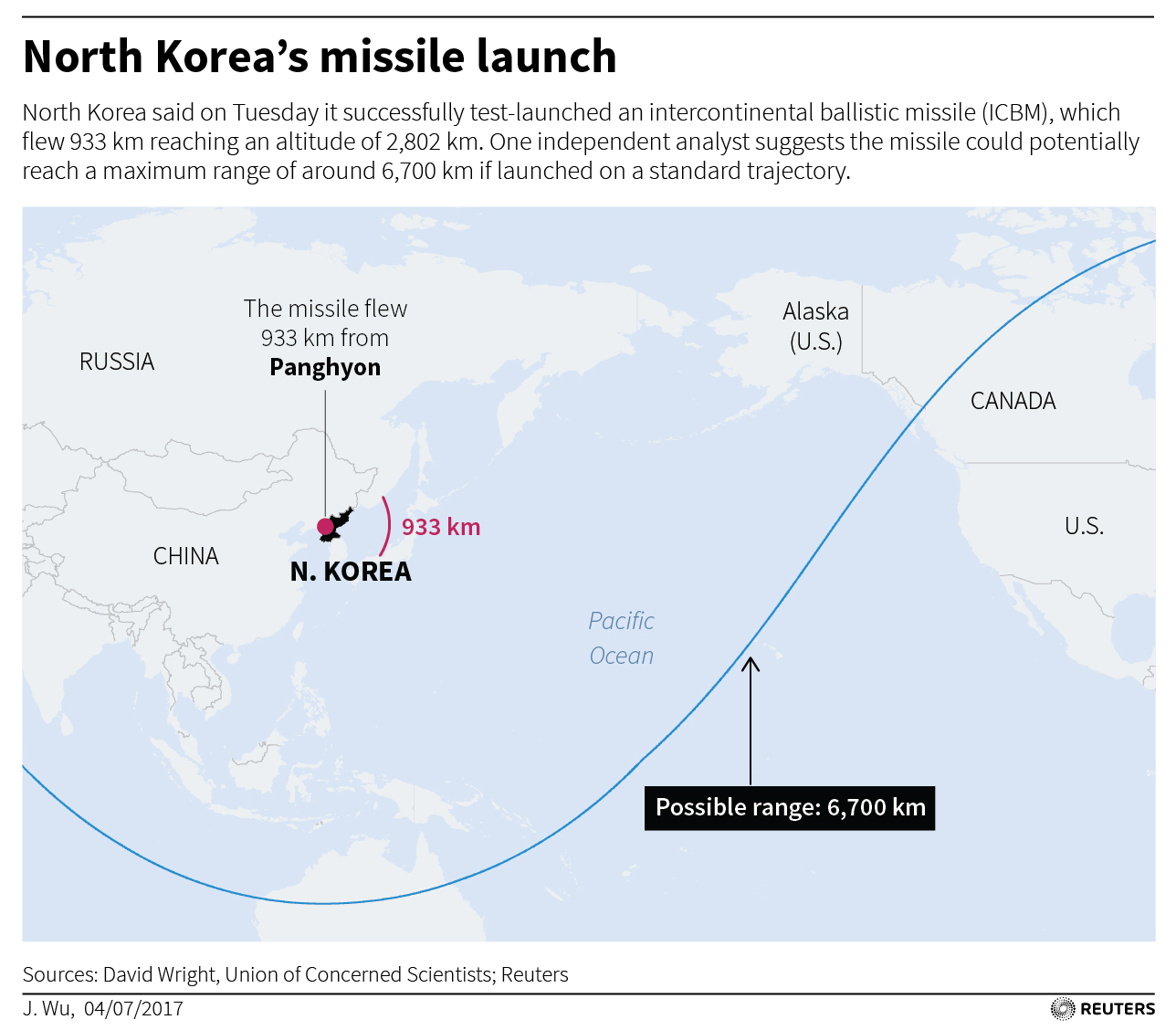
The North’s state media said the missile, Hwasong-14, flew 933 km (580 miles), reaching an altitude of 2,802 km (1,741 miles) in its 39 minutes of flight.
Some analysts said the flight details suggested the new missile had a range of more than 8,000 km (4,970 miles), which would put significant parts of the U.S. mainland in range, a major advance in the North’s program.
The launch was both earlier and “far more successful than expected”, said U.S.-based missile expert John Schilling, a contributor to the Washington-based North Korea monitoring project, 38 North.
It would now probably only be a year or two before a North Korean ICBM achieved “minimal operational capability,” he added.
Experts say a reliable nuclear-tipped ICBM would require a small warhead to fit a long-range missile, technology to protect against intense heat as it re-enters the atmosphere, separate the warhead and guide it to its target.
South Korean President Moon Jae-in, who ordered Wednesday’s drill, said, “The situation was no longer sufficient to respond to the North’s provocation by making statements,” according to his office.
Tuesday’s test poses fresh challenges for Moon, who took office in May with a pledge to engage the North in dialogue while keeping up pressure and sanctions to impede its weapons programs.
His defense minister, Han Min-koo, told parliament on Wednesday there was a high possibility of a sixth nuclear test by the North, but there were no specific indications.
For an interactive graphic on North Korea’s missile program, click http://fingfx.thomsonreuters.com/gfx/rngs/NORTHKOREA-MISSILES/010041L63FE/index.html

(Additional reporting by Lesley Wroughton, David Brunnstrom and Phil Stewart in Washington, and Michelle Nichols in New York and Christian Shepherd in Beijing; Editing by Soyoung Kim and Clarence Fernandez)