By Maher Chmaytelli and Stephen Kalin
MOSUL/ERBIL, Iraq (Reuters) – Iraqi forces slowed their advance on Tuesday through the last streets in Mosul controlled by Islamic State where militants and civilians are packed in densely together, a commander said.
While Iraqi commanders predicted final victory in Mosul this week, U.S.-backed Syrian Democratic Forces announced they had begun an assault on Islamic State’s Syrian redoubt in the Old City of Raqqa.
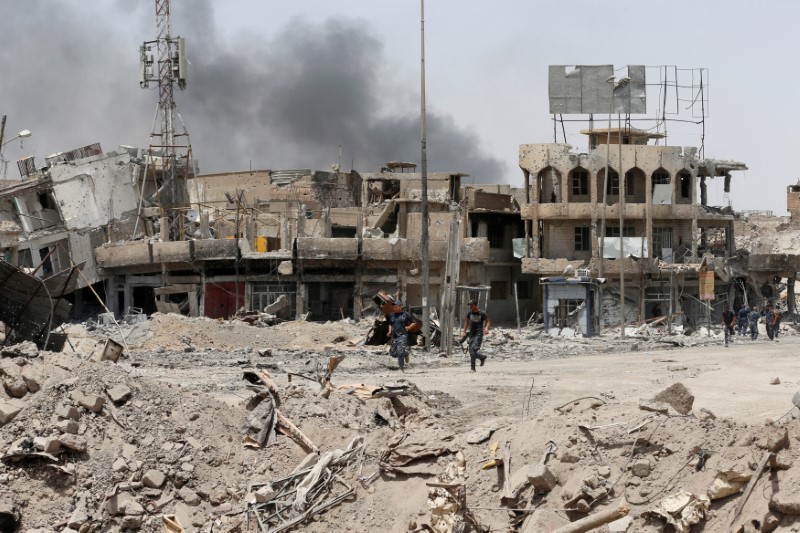
The Iraqi military has pushed insurgents into a shrinking rectangle no more than 300 by 500 meters beside the Tigris river in Mosul; but the resistance has been fierce.
The Rapid Response Division, an elite Interior Ministry unit, called in air strikes just 50 meters away from their targets, and the fighting got close enough at one point for the militants to toss a hand grenade at the troops.
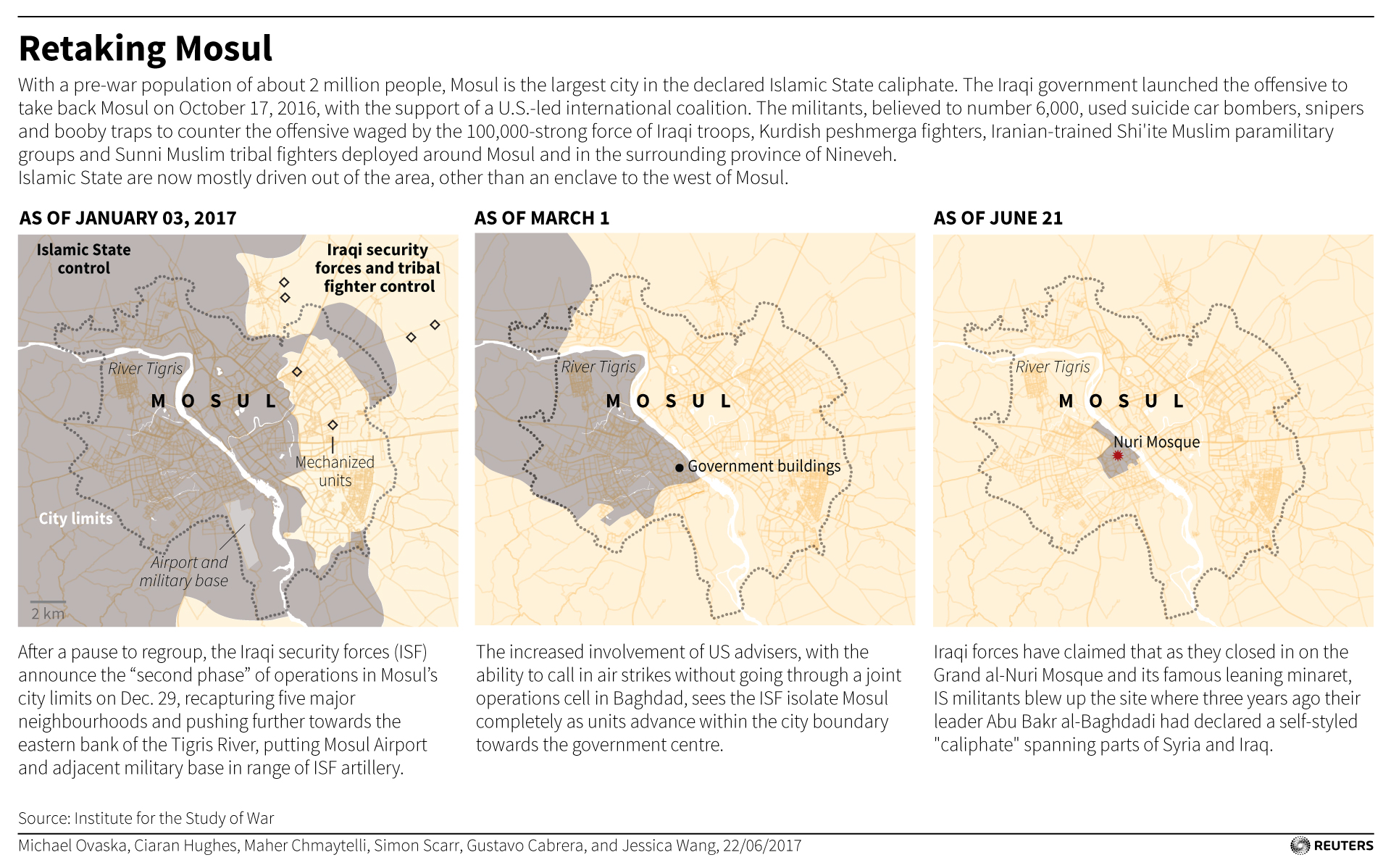
It was from the pulpit of Mosul’s medieval Grand al-Nuri Mosque that, three years ago, leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi declared a “caliphate” over parts of Iraq and Syria. Forces retook the mosque on Thursday, prompting Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi to declare an end to the group’s “state of falsehood”.
The number of Islamic State militants fighting in Mosul, by far the biggest city it has ever controlled, has dwindled from thousands at the start of the U.S.-backed offensive more than eight months ago to a couple of hundred now, according to the Iraqi military.
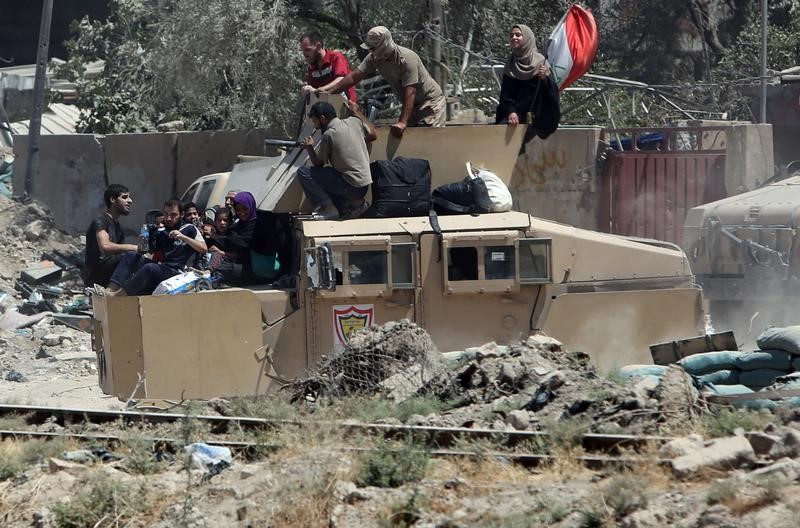
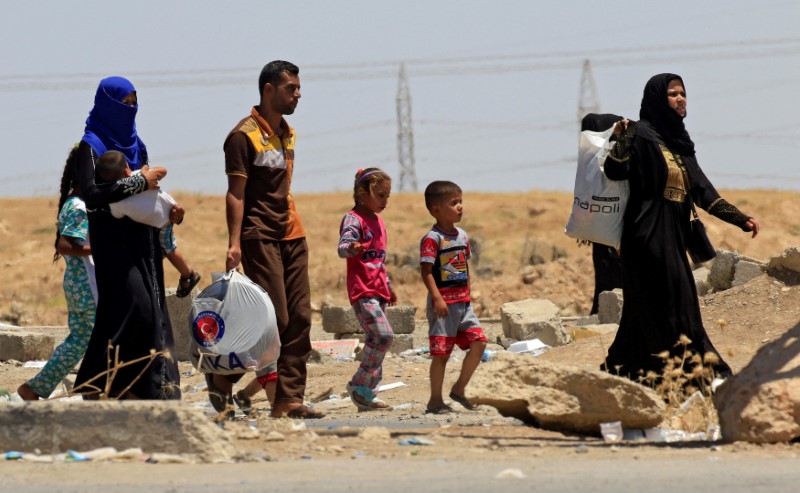
A commander from the Rapid Response Division estimated more than 10,000 civilians remained trapped inside the area under militant control, including people brought from other areas as human shields.
They are trapped with little food, water or medicine amid the Old City’s maze of narrow alleyways, according to residents who have managed to escape.
“The presence of civilians has affected the troops’ advance a lot. The directions from the commander-in-chief of the armed forces are to advance slowly to preserve civilians’ lives and this is what we are doing,” the officer said on state TV without being named.
“The area is small but the advance today is very good, relatively.”
He said the progress had also been slowed by a high number of improvised explosives planted in streets and buildings.
A U.S.-led international coalition is providing air and ground support to the offensive, which Iraq’s army and counter-terrorism service are also fighting in a multi-pronged attack.
TERRITORY SINKING FAST
With Mosul gone, the group’s territory in Iraq will be limited to a few areas west and south of the city where some tens of thousands of civilians live.
In neighboring Syria, a U.S-backed coalition force said it had fired on two small sections of the historic Rafiqah Wall in the Old City of Raqqa, allowing them to overcome Islamic State defenses.
“The portions targeted were 25-metre sections and will help preserve the remainder of the overall 2,500-meter wall,” the coalition said in a statement.
Iraqi authorities are planning a week of nationwide celebrations, to mark the end of the offensive, and Abadi is expected to visit Mosul to formally declare victory.
With its territory shrinking fast, Islamic State has been stepping up suicide attacks in the parts of Mosul taken by Iraqi forces and elsewhere, including a camp for displaced people west of Baghdad on Sunday.
Thousands of people have already fled the Old City this week, joining about 900,000 others, about half the city’s pre-war population, who have been displaced over months of grinding warfare.
Baghdadi has left the fighting in Mosul to local commanders and is believed to be hiding near the Iraq-Syrian border, according to U.S. and Iraqi military sources.
The group has moved its remaining command and control structures to Mayadin, in eastern Syria, U.S. intelligence sources have said, without indicating if Baghdadi was also hiding in the same area.
Baghdadi has often been reported killed or wounded. Russia said on June 17 its forces might have killed him in an air strike in Syria. But Washington says it has no information to corroborate such reports and Iraqi officials are also skeptical.
(Writing by Stephen Kalin; editing by Ralph Boulton)