By Haejin Choi and Heekyong Yang
SEOUL (Reuters) – Long within reach of most conventional North Korean artillery and missiles, South Korea and Japan are far from prepared if an all-out military conflict breaks out as tensions escalate over Pyongyang’s rapidly advancing nuclear weapons program.
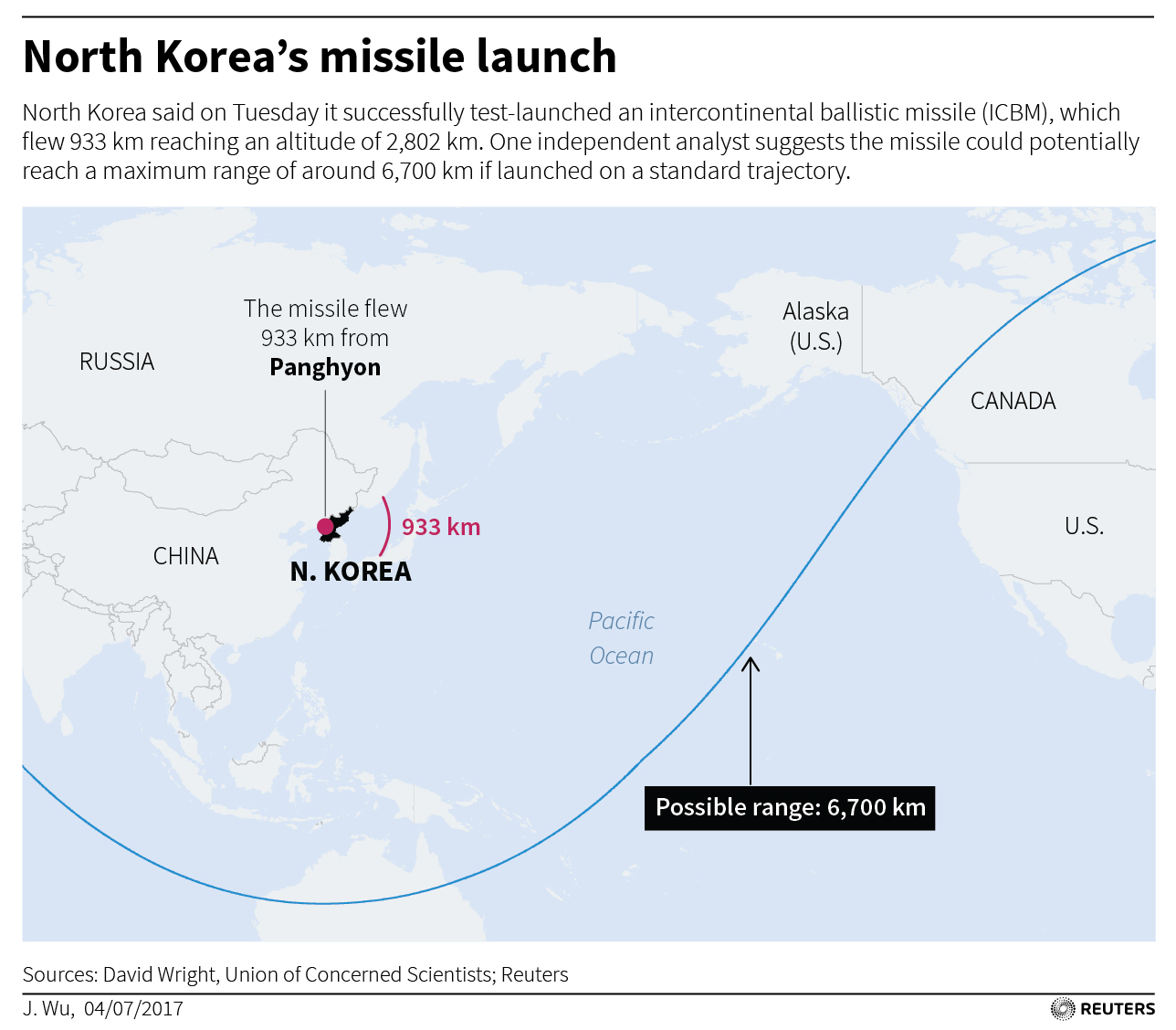
The United States said this week it was ready to use force if necessary to counter the threat from North Korea, which tested an intercontinental ballistic missile that some experts believe has the range to reach Alaska and Hawaii and perhaps the U.S. Pacific Northwest.
North Korea often threatens to strike the neighboring South and Japan, vowing to turn Seoul into a ‘sea of fire’ and ‘a pile of ashes’ the moment it has an order from leader Kim Jong Un.
South Korea has nearly 19,000 bomb shelters throughout the country. They include more than 3,200 in Seoul, just 40 km (25 miles) from the militarized border drawn up under a truce that stopped the 1950-53 Korean War but left the combatants technically at war.
Chung Yoon-jin, a university student in Seoul, had no clue these shelters existed.
“I have never seen any signs that say ‘shelter’, although I have been to lots of places in Seoul,” the 26-year-old Chung said.
The shelters are not built to protect against nuclear, chemical or biological attacks. They are mostly in subway stations or basements and parking garages in private apartments and commercial buildings designated as shelters with the consent of the owners.
For a graphic on the locations of the shelters, click http://tmsnrt.rs/2rW8uvn
In Seoul, most bomb shelters have no long-term supplies of food, water, medical kits or gas masks, an official at Seoul Metropolitan Government told Reuters. They can’t be forced to stock up because no public funding is provided, said the official who declined to be identified.
In Tokyo, the Japanese capital of 13.5 million people has an unknown number of bomb shelters left from World War II, but they are not useable or accessible to the public, an official at Tokyo Metropolitan Government’s disaster prevention department told Reuters.
Tokyo has no plans to reuse the decades-old shelters or build new ones for now.
“The extent of any damage that could be caused by a North Korean missile is still unknown, and it will take time to figure out an appropriate design for a shelter,” the official said.
OBLIVIOUS TO MISSILE THREAT
While residents in Alaska and Hawaii are just waking up to the possibility of living within range of a North Korean missile, South Koreans for years have been exposed to thousands of artillery massed an hour’s drive or so from the border, in addition to short-range missiles and bombs.
People have grown numb to Pyongyang’s unprecedented pace of missile and nuclear tests since the beginning of last year.
“Every time, nothing seems to happen after (North Korea provocation), so now I feel I’m used to it. I think to myself, nothing will happen,” said Suh Yeon-ju, a 30-year-old housewife.
Unlike in Japan, where sales of private nuclear shelters and radiation-blocking air purifiers have risen in recent months, South Korea has no market for private bunkers.
One public bomb shelter that Reuters visited in central Seoul was in a large underground parking garage a few steps from a government complex building. A small sign posted at the entrance indicated a shelter, but people inside had no clue.
A person in charge of the parking garage said one day last year he came to the office and saw a “shelter” sign posted, but he had no idea what it was.
To raise awareness, Seoul has handed out 34,000 paper fans this summer with information about bomb shelters, and is in the process of creating other promotional products such as flyers and stickers, the city government official said.
But it’s difficult to get the buildings hosting shelters to put easily seen directional signs, he said.
Shin Ji-ha, a 24-year-old university student in Seoul, said she heard about bomb shelters but didn’t know where they were. It didn’t matter to her anyway.
“I would be dead like in less than a second (if a war broke out),” she said. “There will be no pain at all so I don’t mind that much.”
For a graphic on threat to Seoul, click http://fingfx.thomsonreuters.com/gfx/rngs/NORTHKOREA-MISSILES/010041BR2VH/index.html
(Additional reporting by Yuna Park, Christine Kim, Dahee Kim and Se Young Lee in Seoul, Megumi Lim in Tokyo; Writing by Soyoung Kim; Editing by Bill Tarrant)